They say beauty comes from within—and when it comes to your skin, that couldn’t be more true. While serums and creams play a role in maintaining a radiant complexion, the foundation of healthy skin is built from the inside out. Your diet and supplement choices can enhance collagen production, fight oxidative stress, and maintain hydration—especially when tailored to your genetic blueprint.
Part 1 of this series explored how genomics unlocks a deeper understanding of your skin’s unique needs. Now, let’s dive into how nutrition and supplements can optimize your skin health based on what your DNA reveals.
The Connection Between Diet, Supplements, and Skin Health
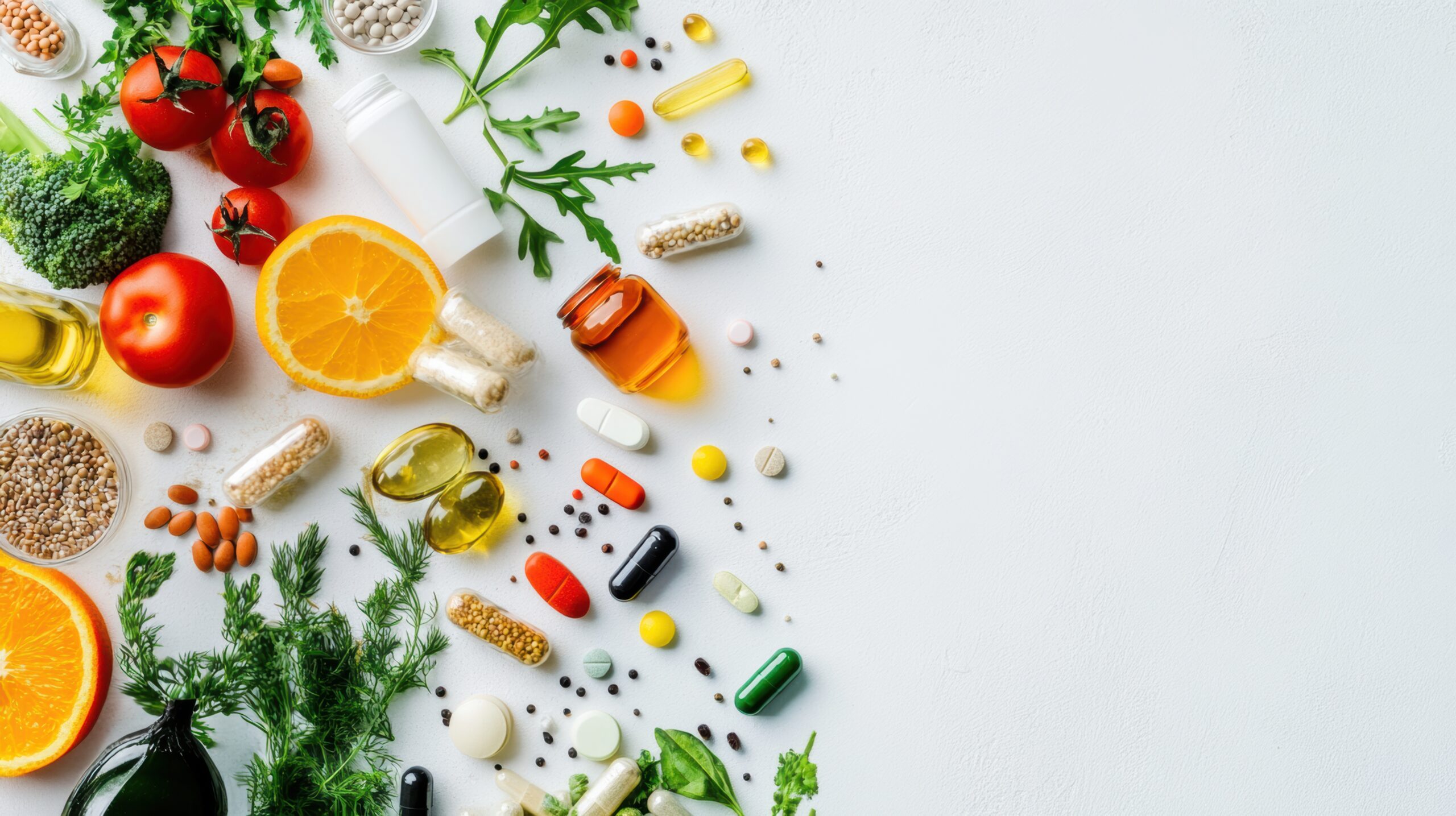
Your skin is the largest organ in your body, and just like any other organ, it thrives when adequately nourished. Nutrients support collagen synthesis, reduce inflammation, and protect against environmental stressors. Deficiencies in key vitamins, minerals, and fatty acids can accelerate signs of aging, dryness, and sensitivity.
Genetic testing can help identify areas where your skin may need extra support. For example, if your genes indicate lower collagen synthesis, a diet rich in Vitamin C and collagen peptides can be particularly beneficial. Increasing your antioxidant intake can help protect against premature aging if you are predisposed to oxidative stress.
Key Nutrients for Optimal Skin Health
Collagen Boosters – Strengthen and Support Skin Structure
If your DNA suggests lower collagen production, focus on:
- Vitamin C – Essential for collagen synthesis and skin repair. It is found in citrus fruits, bell peppers, strawberries, and kiwi.
- Collagen Peptides – Hydrolyzed collagen from bone broth, marine collagen supplements, and grass-fed gelatin supports skin elasticity.
- Zinc – Aids in collagen formation and wound healing. Sources include pumpkin seeds, lean meats, shellfish, and lentils.
- Silica – Helps maintain skin firmness and hydration. It is found in cucumbers, bell peppers, oats, and horsetail extract.
Hydration & Skin Barrier Support – Prevent Dryness and Improve Elasticity
If your genes show a predisposition to dry skin, prioritize:
- Hyaluronic Acid – Attracts and retains moisture in the skin. Found in bone broth and available as a supplement.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids – Essential for maintaining the skin’s lipid barrier and reducing inflammation. Sources include salmon, flaxseeds, walnuts, and chia seeds.
- Ceramides – Strengthen the skin barrier and lock in hydration. Found in wheat germ, brown rice, and sweet potatoes.
- Gamma-Linolenic Acid (GLA) is an omega-6 fatty acid that improves skin hydration. Found in evening primrose oil and borage oil.
Antioxidant Protection – Combat Free Radicals and Premature Aging
If your DNA suggests lower antioxidant capacity, include:
- Vitamin E – Protects against oxidative damage and supports skin healing. Found in almonds, sunflower seeds, avocados, and spinach.
- Polyphenols – Plant compounds that neutralize free radicals. Rich sources include green tea, dark chocolate, berries, and pomegranates.
- Resveratrol – A powerful anti-aging compound. Found in red grapes, blueberries, and red wine (in moderation).
- Glutathione – A master antioxidant that brightens skin and detoxifies cells. Naturally present in asparagus, avocados, and available as a supplement.
Blood Sugar & Glycation Defense – Protect Against Sugar-Induced Aging
If your genetic markers indicate a risk for glycation (sugar-damaging collagen), consider the following:
- Reducing Refined Sugars – Minimize processed sugars and opt for low-glycemic foods like whole grains, leafy greens, and berries.
- Alpha-Lipoic Acid (ALA) – A potent antioxidant that combats glycation damage. It is found in spinach and broccoli and is a supplement.
- Cinnamon & Chromium – Improve blood sugar regulation, reducing the risk of glycation-related skin aging. It is found in cinnamon, broccoli, and nuts.
Microbiome & Gut-Skin Connection – Balance Inflammation and Skin Conditions
If you’re prone to inflammation or skin conditions like acne or eczema, support gut health with:
- Probiotic-Rich Foods – Enhance the skin-gut connection and reduce inflammation. Found in yogurt, kimchi, sauerkraut, and kefir.
- Prebiotic Fibers – Nourish beneficial gut bacteria. It is found in garlic, onions, bananas, asparagus, and leeks.
- L-Glutamine – Supports gut lining integrity and reduces systemic inflammation. Available as a supplement.
- Zinc & Vitamin D – Both play a role in immune function and skin healing. It is found in oysters, eggs, mushrooms, and fortified dairy.
How to Personalize Your Skincare Nutrition Plan
1️⃣ Get a Genetic Skin Test – A test like Spotlight on Skin provides insights into your unique genetic markers and skin health predispositions.
2️⃣ Adjust Your Diet Accordingly – If genetically predisposed to oxidative stress, focus on antioxidant-rich foods. If collagen degradation is a concern, increase your intake of collagen-supporting nutrients.
3️⃣ Incorporate Targeted Supplements – While whole foods should be your foundation, supplements can fill the gaps based on your genetic needs.
4️⃣ Monitor Your Skin’s Response – Nutrition-based changes take time. Stick with your tailored plan for at least 8–12 weeks to see noticeable improvements in skin texture, hydration, and overall radiance.
Final Thoughts: The Future of Skincare is Inside-Out
Skincare is not just about what you apply but about what you consume. Understanding your genetic blueprint and nourishing your skin from within can slow aging, maintain a strong skin barrier, and achieve a lasting natural glow.
In Part 3 of this series, we’ll explore creating a skincare routine that aligns with your genetic insights, combining the best topical treatments and internal nourishment.